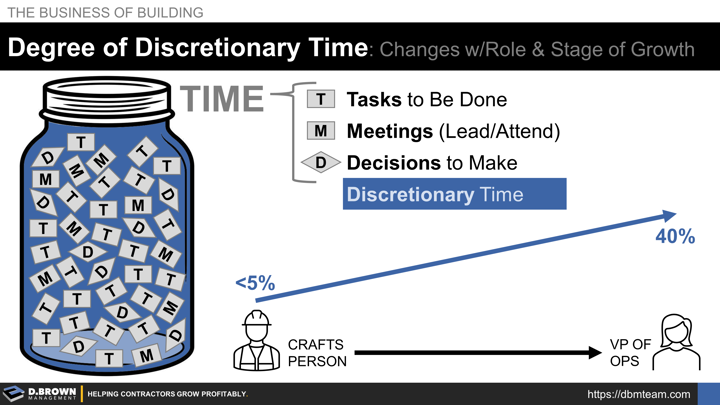
A job role is mostly a collection of:
- Tasks to be done.
- Meetings to lead or attend.
- Decisions to make.
These are part of the management system for the project and/or company. They have standards of performance defined to some degree ranging from a simple thumb up/down through to clearly defined procedures and outcome expectations with variability tolerances.
These are logically grouped into a role based on similar timing, location, tools/equipment, and skill levels.
Deciding when these happen is the degree of discretionary scheduling for the role.
What is left over after all these standards are met is the discretionary time of the role. This time is used for anything from spending extra time in certain areas beyond the standard, development for future role(s), or exploring completely different options for markets or operations.
As a job role level grows, the percentage of discretionary time increases. For example, a crafts person likely has 5% or less of discretionary time. They are laid out to do their work by the Foreman or Crew Leader each day with the objective of maximum Time-on-Tools.
A VP of Operations may have 40% of their time as discretionary. Some of that time may be directed towards company improvement initiatives they are accountable.
As a contractor grows through different stages of growth, similar job roles will have progressively less discretionary time as the role gets more clearly defined. For example, an Operations Manager who is the first to hold that role in a stage 2 or 3 sized company will likely be defining the role while doing it - nearly 100% discretionary time.
A VP of Operations with a stage 6 company may have a span-of-control 3X larger than a stage 3 contractor and will likely only have about 40% discretionary time as much of their role has been defined as standard work. That stage 6 company will have 3-5 people doing this same role which is why a higher degree of standardization is required.
One is not better or worse than the other. It is just differences in stages of growth and career development.